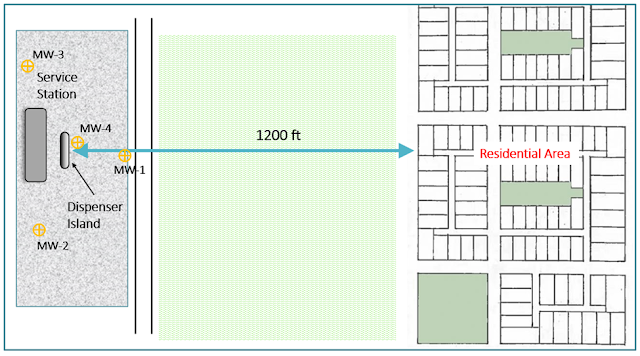
A
1-D analysis of contaminant transport often greatly overestimates plume extent,
resulting in an overly-conservative assessment.
A common question related to contaminant plumes: “How far downgradient will the plume extend?”
We
may want to know this for several reasons:
•
Will
the plume reach a receptor at some distance from the source?
•
How
far should I place monitoring wells to measure the plume?
•
And
in some states (e.g. NJ) how far should I draw the boundary of the groundwater Classification
Exception Area (CEA).
Possible
Methods
To
analyze plume extent from the source over time, we can perform screening
analyses using models ranging from simple analytic 1-D solutions, to 3-D analytic and
semi-analytic solutions. We could also use more costly and sophisticated 3-D
numerical fate and transport models - - but to examine the difference between a
1-D model and a 3-D model, analytical solutions are perfectly capable analysis
tools.
1-D
Plume Transport Modeling
For
many decades, from the 1970s through present, investigators and regulators have often explored the movement of a dissolved chemical plume extending downgradient
from a steadily-releasing source using some form of mathematical solution to
the 1-D transport equation (e.g. Ogata and Banks 1961; Bear 1972 & 1979). The
often cited Ogata and Banks 1961 solution is a simple representation of
advective-dispersive transport that does not incorporate the processes of
adsorption (retardation) nor degradation. The Bear 1972 & 1979 solutions
are more useful because they incorporate the effects of dispersion,
retardation, and degradation.
1-D Example Application
To
illustrate the plume length that a 1-D model would calculate, a simple example
was developed in which the Bear 1-D transport solution was used to calculate the
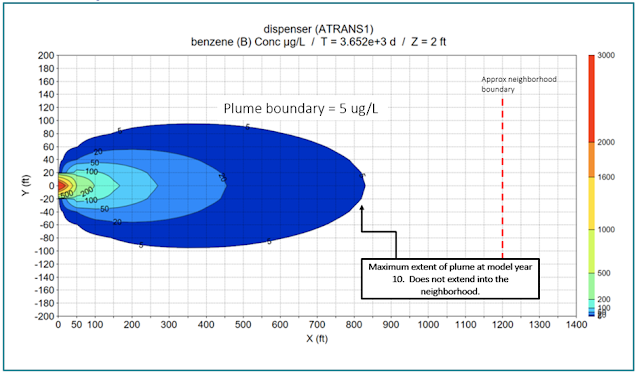
location of the 5 ug/L plume boundary of a benzene plume 5880 days (16 years)
after release (Fig 1). Source benzene concentration was assumed to remain
constant at 1000 ug/L; groundwater velocity was set to 1 ft/d and retardation
factor was set to 2; 1-D aquifer dispersivity was 50 ft; and a conservative
benzene plume half-life of 2 years was applied.
 |
| Fig 1. 1-D calculation shows plume extends 2900 ft from the source after 5880 days. |
3-D
Plume Transport Modeling
Another
approach often employed by investigators or regulators is to begin with the
full 3-D transport equation and apply that 3-D solution to calculate
concentration along the centerline of the plume to determine the extent of the
plume in the downgradient direction.
One
of the widely known solutions to the 3-D transport equations was developed by
Domenico in 1987. This solution forms the basis for a number of models used by
regulatory agencies to estimate contaminant plume movement:
•
BIOSCREEN
developed by USEPA (see USEPA website for BIOSCREEN v1.4)
•
BIOCHLOR
(USEPA) v 2.2
•
Quick
Domenico model described by PADEP in certain of its regulatory documents (see
PADEP website Quick Domenico spreadsheet model)
3-D Example Application
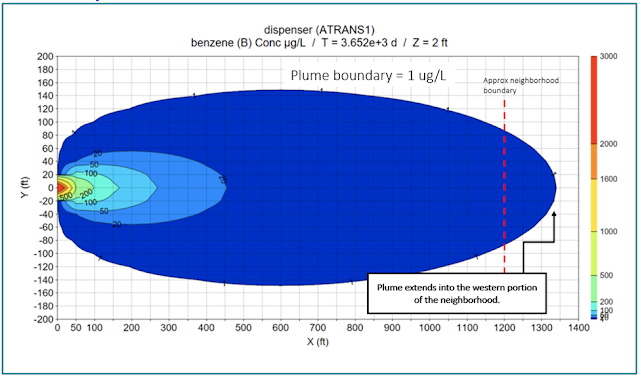
So, we can now solve the same plume transport problem illustrated in Fig 1, but we will instead use the 3-D Domenico solution model (instead of 1-D). Transverse dispersivity is
set to 1/10th the longitudinal dispersivity and vertical dispersivity is
set to 1/1000th the longitudinal dispersivity (these parameters were not present in the 1-D model). The 3-D transport solution
calculates a much shorter plume length; 1280 ft versus the 1-D length of 2900 ft
(Fig 2).
 |
| Fig 2. 3-D calculation shows plume extends 1280 ft from the source after 5880 days. |
Newer
3-D Methods
Analytical
In
recent years minor discrepancies have been reported between the Domenico solution
and more rigorous solutions to the 3-D transport equations (see for example (Guyonnet
and Neville 2004; West et al 2007; Srinivasan et al 2007; Karanovic et al 2007;
Devlin et al 2012). The discrepancies occur primarily along the centerline axis
of the plume; this means that errors may be introduced when attempting to
estimate the plume length (i.e. how far downgradient from the source
contamination may extend).
Several
investigators have modified the original Domenico 3-D transport solution to
attempt to mitigate the errors caused by the original formulation. For example:
•
BIOSCREEN
(USEPA) was updated to BIOSCREEN-AT (Karanovic & Neville 2007)
•
Srinivasan,
Clement & Lee (2007) published an updated version of the Domenico solution
Semi-Analytical
The
1-D and 3-D solutions we have examined to this point are analytic solutions.
Certain simplifications are made in the formulation of the transport
differential equation that allows it to be solved in closed form - - i.e. the
solution does not contain an integral term; the algebraic equation can be
solved in a spreadsheet
There
is a class of more rigorous solutions that are not simplified and still contain
an integral term; and because of that, they are more accurate. These solutions are
typically solved in a simple program that employs a numerical integration
routine to arrive at the calculated concentrations.
Examples
of these semi-analytical transport models include:
•
ATRANS
•
BIOSCREEN-AT
(Domenico 1987 solution modified by Karanovic et al 2007)
•
3DADE
(USDA 1994)
•
N3DADE
(USDA 1997)
•
AT123D-AT
(Yeh 1984 solution modified by Burnell et al 2012)
These
solutions have been assembled into a unified user interface in TS-CHEM. They
provide a means of calculating more accurate estimates of contaminant plume
extent for environmental assessments.
To summarize: Contaminant
plume analyses based on 1-D models are likely to greatly overestimate plume
extent. This may result in an overly-conservative assessment that causes
concern, or results in actions, related to impacts that are not likely to
occur. More accurate evaluations of plume extent can be calculated using 3-D
contaminant transport model. TS-CHEM provides a library
of over 30 analytical 3D plume transport solutions for making these types of evaluations.
To learn more about TS-CHEM, or to download a FREE DEMO VERSION of the software, visit the TS-CHEM Website today!